 Motivation behind Simulated Annealing:
Motivation behind Simulated Annealing:
 Motivation behind Simulated Annealing:
Motivation behind Simulated Annealing:
|
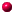
| An analogy to SA: shaking a bottle to increase its content's density. |
 Basic Terms of SA:
Basic Terms of SA:
 maps an
input vector
maps an
input vector
 into a scalar
E:
into a scalar
E:

where each
 is viewed as a point in an input space.
The task of SA is to sample the input space effectively to
find an
is viewed as a point in an input space.
The task of SA is to sample the input space effectively to
find an
 that minimizes E.
that minimizes E.
 specifies the probability density function of the difference
between the current point and the next point to be visited.
Specifically,
specifies the probability density function of the difference
between the current point and the next point to be visited.
Specifically,
 (
( )
is a random variable with probability density function
)
is a random variable with probability density function
 ,
where T is the temperature.
For common SA (especially when used in combinatorial
optimization applications),
,
where T is the temperature.
For common SA (especially when used in combinatorial
optimization applications),
 is usually a function independent of the temperature T.
Acceptance function:
After a new point
is usually a function independent of the temperature T.
Acceptance function:
After a new point
 has been evaluated,
SA decides whether to accept or reject it
based on the value of an acceptance function
has been evaluated,
SA decides whether to accept or reject it
based on the value of an acceptance function
 .
The most frequently used acceptance function is the
Boltzmann probability distribution:
.
The most frequently used acceptance function is the
Boltzmann probability distribution:

where c is a system-dependent constant,
T is the temperature, and
 is the energy difference between
is the energy difference between
 and
and
 :
:

The common practice is to accept
 with probability
with probability
 .
Note that when
.
Note that when
 is negative, SA tends to accept the new point because it
reduces the energy. When
is negative, SA tends to accept the new point because it
reduces the energy. When
 is positive, SA may accept the new point and end up in a
higher energy state. In other words, SA can go either uphill
or downhill; but the lower the temperature, the less
likely SA is to accept any significant uphill actions.
is positive, SA may accept the new point and end up in a
higher energy state. In other words, SA can go either uphill
or downhill; but the lower the temperature, the less
likely SA is to accept any significant uphill actions.
 SA Flowchart:
SA Flowchart:
![]()
![]()
where
![]() (
(![]() )
is the deviation of the new point from the current one,
T is the temperature, and n is the dimension
of the space under exploration.)
)
is the deviation of the new point from the current one,
T is the temperature, and n is the dimension
of the space under exploration.)
![]()
 SA for Discrete (Combinatorial) Optimization: An Example:
SA for Discrete (Combinatorial) Optimization: An Example:
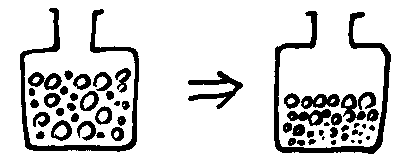
Travel Salesperson problem (TSP):
how to transverse n cities
once and only once with the minimal total distance?
|
| Travel salesperson problem |
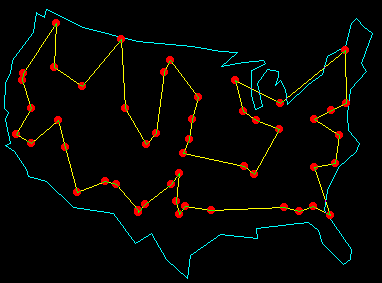
|
| Three possible types of move sets for travel salesperson problem |
|
|
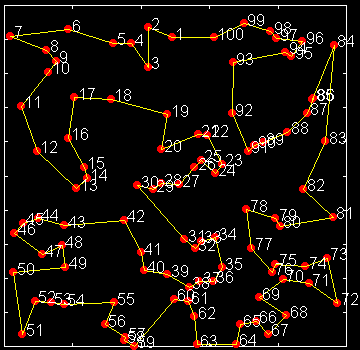
|
| Initial random path | A path during SA process | Final path after SA process |
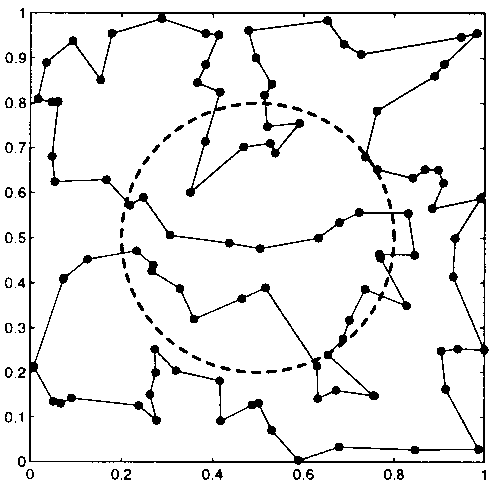
|
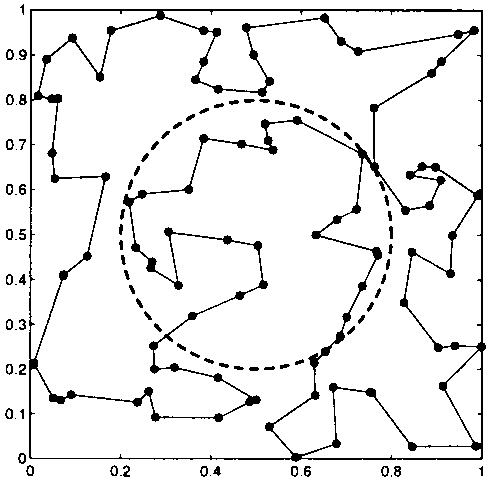
|
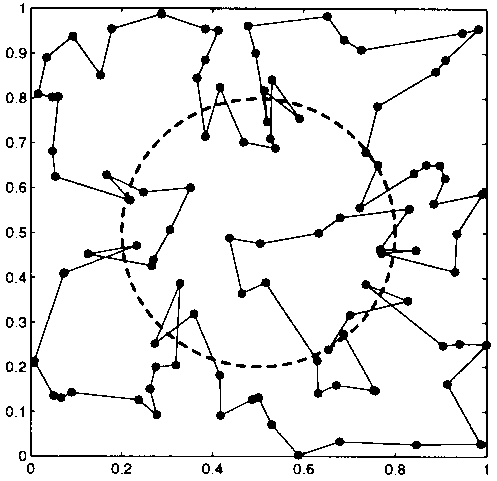
|
| Cost of cross the circle = 0 | Cost of cross the circle = 0.5 | Cost of cross the circle = -0.3 |
 Advantages of SAs:
Advantages of SAs:
 Weakness of SA:
Weakness of SA:
 Reported SA Applications:
Reported SA Applications:
 Reference:
Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing
Reference:
Neuro-Fuzzy and Soft Computing