Histogram-based Interest Points Detectors
Wei-Ting Lee Hwann-Tzong Chen
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
- Abstract
- We present a new method for detecting interest points using histogram information. Unlike existing interest point detectors, which measure pixel-wise differences in image intensity, our detectors incorporate histogram-based representations, and thus can find image regions that present a distinct distribution in the neighborhood. The proposed detectors are able to capture large-scale structures and distinctive textured patterns, and exhibit strong invariance to rotation, illumination variation, and blur. The experimental results show that the proposed histogram-based interest point detectors perform particularly well for the tasks of matching textured scenes under blur and illumination changes, in terms of repeatability and distinctiveness. An extension of our method to space-time interest point detection for action classification is also presented.
- Image matching
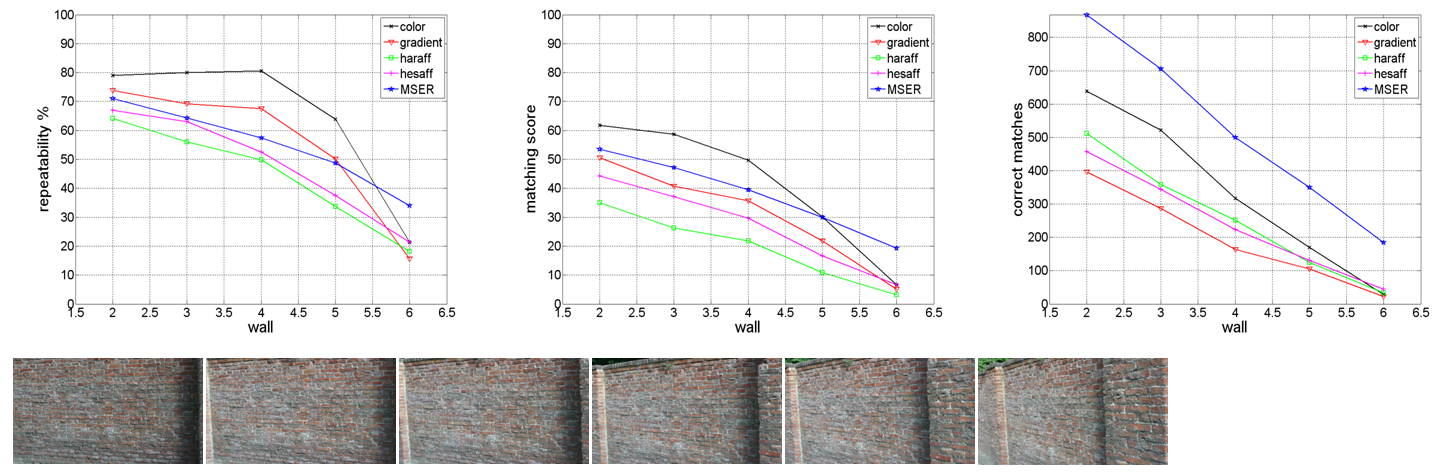
- The proposed detectors achieve good performance for the tasks of matching textured scenes, e.g., the 'wall' sequence and the 'trees' sequence shown below (click to enlarge). The performance is evaluated by the repeatability and the matching score, using the code and datasets created by Mikolajczyk et al.. The black lines are the results of the color-histogram detector; the red lines are obtained by the oriented-gradient-histogram detector. More evaluation results can be found in our paper.
- Action classification with space-time histogram-based interest points
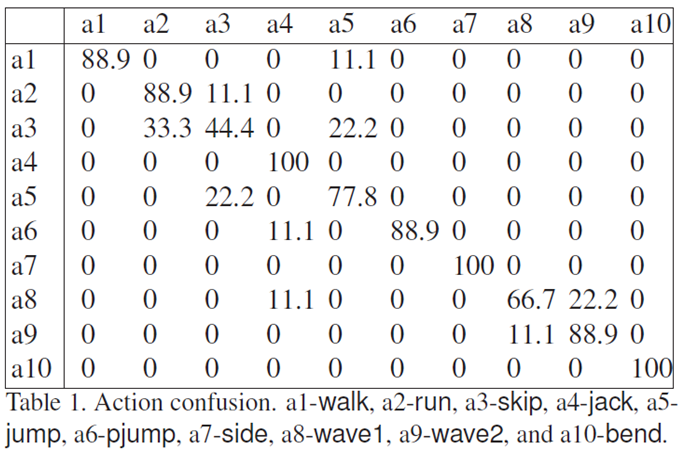
- We extend the histogram-based method to the detection of space-time interest points, and apply the detector to action classification. We use the human action database provided by Gorelick et al. for evaluation. The database contains ten types of actions, and for each action we use nine videos of the same action performed by different people. We ignore the silhouette information since our method does not assume a known background. The result of leave-one-out test is shown below in the confusion matrix.
- Paper
- Wei-Ting Lee, Hwann-Tzong Chen: Histogram-based Interest Point Detectors. CVPR 2009.
- Code
- Here is a Matlab implementation of the histogram-based interest point detectors. The detectors can be plugged into the evaluation code provided by Mikolajczyk et al. to compute the repeatability and the matching score of image matching.
Last updated: 14 August 2009